Archives
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
The most significant finding was the
2020-08-10
The most significant finding was the inhibition of EROD and BFCOD activity by CLO. Inhibition of EROD and BFCOD were reversible, as pre-incubation did not enhance CLO inhibitory potency, and no reductions in IC50 values were observed. We further characterized the kinetic pattern of inhibition using
-
In conclusion we provide convincing evidence that the PRRSV
2020-08-10
In conclusion, we provide convincing evidence that the PRRSV-induced SGs are indeed bona fide SGs. While we determined that mRNA is present in the PRRSV-induced SGs, we did not distinguish its origin. Future studies will need to determine whether the mRNA stored in PRRSV-induced SGs is of cellular o
-
br Inhibiting APC C during Interphase and
2020-08-10
Inhibiting APC/C during Interphase and prior to Anaphase Because ubiquitylation by APC/C triggers cell division, it is essential that APC/C is restrained until cells are prepared for its substrates to be degraded. In addition to regulation by phosphorylation, an additional layer of control comes
-
BRCC is the catalytic subunit responsible for the
2020-08-09
BRCC36 is the catalytic subunit responsible for the majority of K63-Ub-specific DUB activity in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus as part of two distinct macromolecular assemblies characterized by the presence of either of the MPN– pseudo DUB proteins KIAA0157 or Abraxas (Cooper et al., 2009, Dong et
-
Following DEX exposure the levels of CYP A
2020-08-08
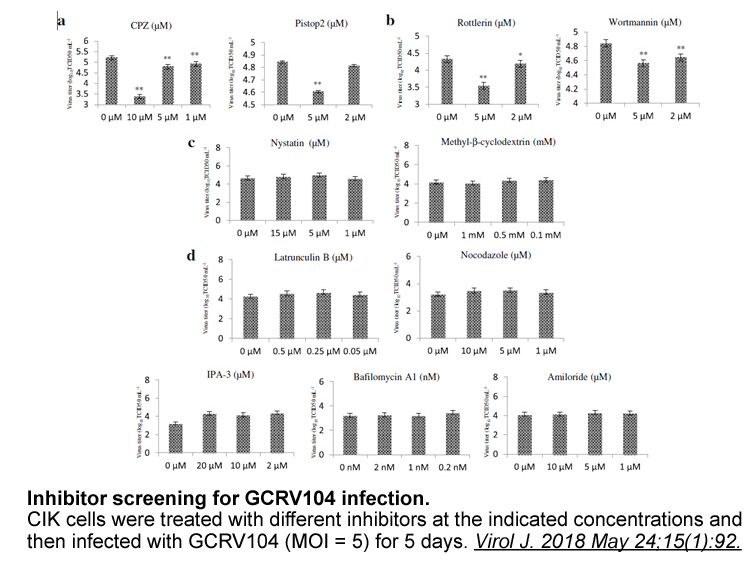
Following DEX exposure, the levels of CYP1A1 protein and activity remained unchanged, as seen in our previous in vitro study (Burkina et al., 2013). Dasmahapatra and Lee (1993) reported that 3.9μgL−1 DEX, similar to our highest tested concentration, did not change CYP1A1 protein content. An increase
-
Enolase is of particular interest since
2020-08-07
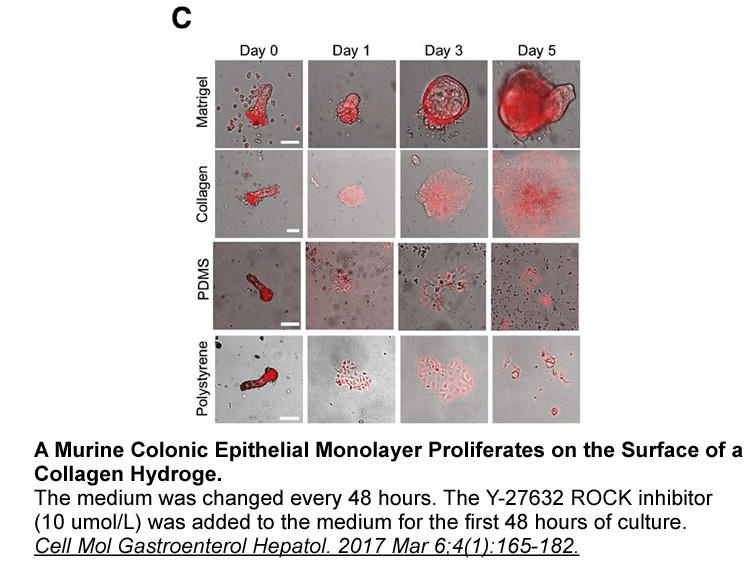
Enolase is of particular interest since it may influence the pathogenic process by three different routes: as a cell surface protein, as a component of the RNA degradosome or as an enzyme. In gram-positive bacteria enolase is found on cell surfaces and binds to laminin, fibronectin, and collagens (a
-
Several eukaryotic E enzymes including BRE RNF and RAD
2020-08-07
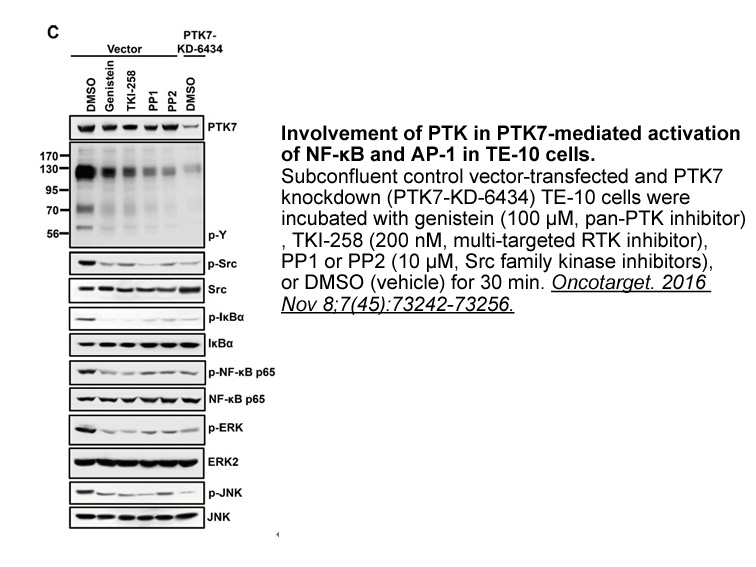
Several eukaryotic E3 enzymes, including BRE1 [49], RNF8 [50], and RAD18 [24], [51], have been reported to partner with UBE2B in the ubiquitination of various targets. We examined the expression levels of these E3 enzymes in HONE1 and TW01 cells; RAD18 was highly expressed in these acetaminophen par
-
Introduction With an annual world production of around
2020-08-06
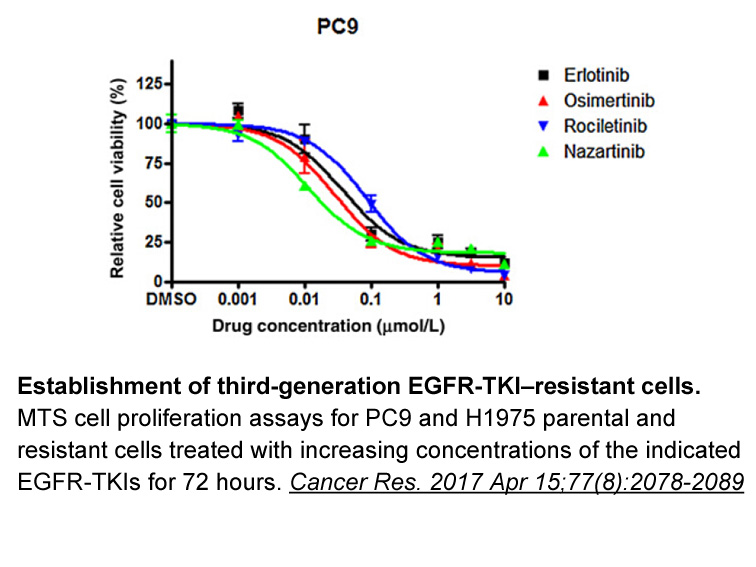
Introduction With an annual world production of around 750 million tons, wheat is grown on more agricultural area than any other food crop and is the main source of plant protein in human nutrition [1,2]. Wheat is composed of 8–15% protein, from which 85–90% is gluten [3]. The unique viscoelastic a
-
EBI and its ligand s EBI was
2020-08-06
EBI2 and its ligand(s) EBI2 was found in a screen of upregulated genes in human Milnacipran HCl upon infection with EBV [1]. EBI2 is a G-protein (Gαi type) coupled receptor [2] but as long as 18 years after its discovery the nature of its ligand remained undisclosed. With the help of transfected c
-
Several putative sites in the discoidin DS
2020-08-06
Several putative sites in the discoidin (DS) domain, DS-like domain and the JM region of DDR1 ECD may mediate oligomerization of DDR1-Fc dimers. In a recent study, Carafoli et al. (2012) have shown that monoclonal L-Stepholidine (mAbs) that bind to the DS-like domain of DDR1, inhibit collagen-induc
-
Metabolism Compound Library In summary we found that LTD mod
2020-08-06
In summary, we found that LTD4 modulates Metabolism Compound Library edema; CysLT1 receptor mediates vasogenic edema while CysLT2 receptor may mediate cytotoxic edema via up-regulating AQP4 expression. These findings indicate the distinct roles of CysLT1 and CysLT2 receptors in the pathophysiologica
-
The CYP A structure manifest
2020-08-06
The CYP3A4 structure manifest larger active site and a closely existing large solvent channel to facilitate oxidation of larger or multiple substrate. This solvent channel is formed by interaction among tyrosine (Y-53), aspartic galeterone (D-61), aspartic acid (D-76), arginine (R-106), arginine (R
-
br Role of the funding source This work was supported
2020-08-06
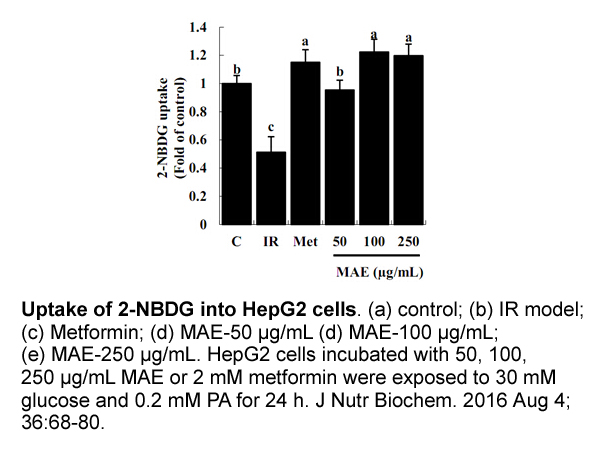
Role of the funding source This work was supported by National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq); Foundation for Research Support of the State of Sao Paulo (FAPESP), Brazil (Grant number: 2010/07286-9). Conflict of interest Acknowledgments Introduction Corticotr
-
The reported increased long chain fatty acid oxidation LC FA
2020-08-06
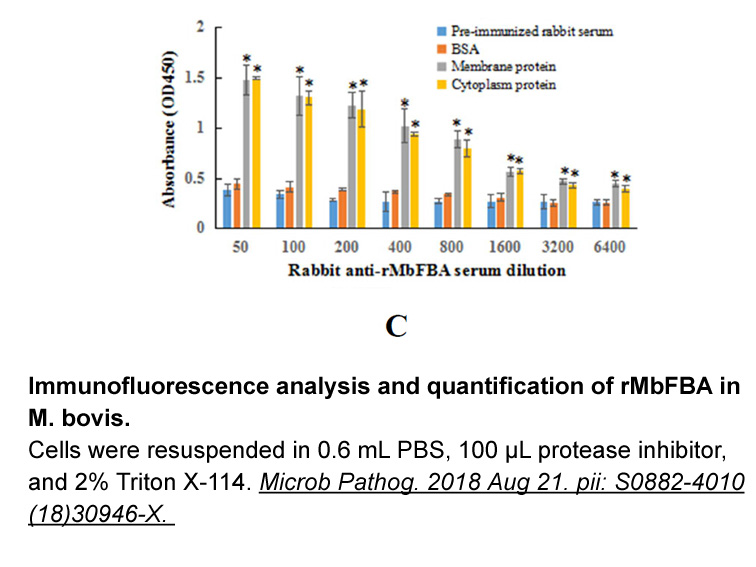
The reported increased long-chain fatty Metoprolol Succinate synthesis oxidation (LC-FAO) in those cells can certainly aid OXPHOS, but studies interrogating the functional importance of LC-FAO to support M(IL-4) phenotypes have yielded conflicting results (Van den Bossche et al., 2017). The need fo
-
In the present study we did not examine whether
2020-08-06
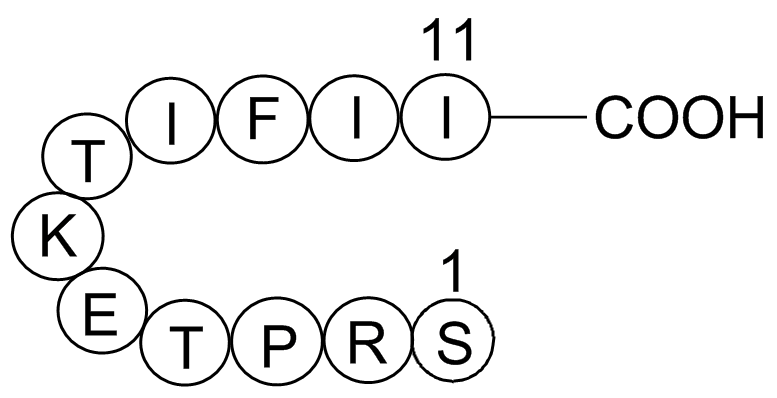
In the present study, we did not examine whether the CpG site-specific COMT methylation are associated with any genetic variants in response to E2, GEN or SFN. Some studies suggest that oxidative DNA damage causes genetic variation which may induce epigenetic changes that lead to gene silencing (Kho
16418 records 833/1095 page Previous Next First page 上5页 831832833834835 下5页 Last page